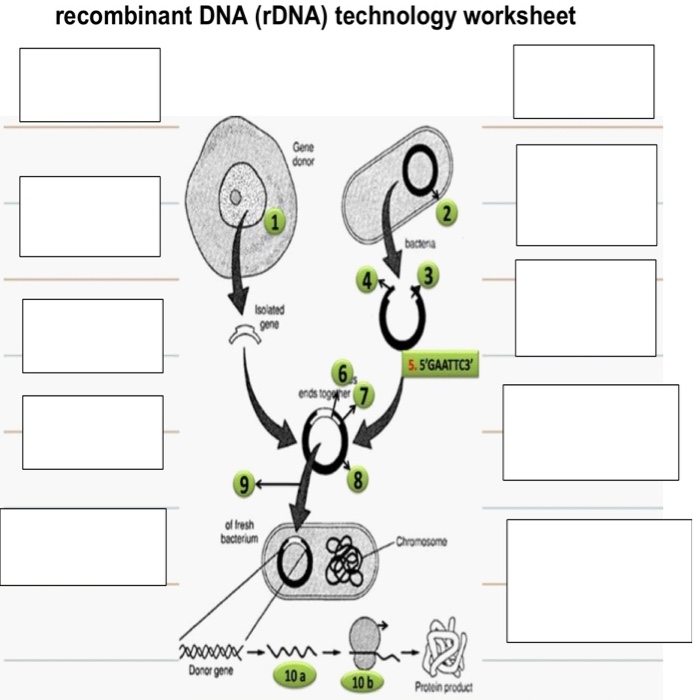
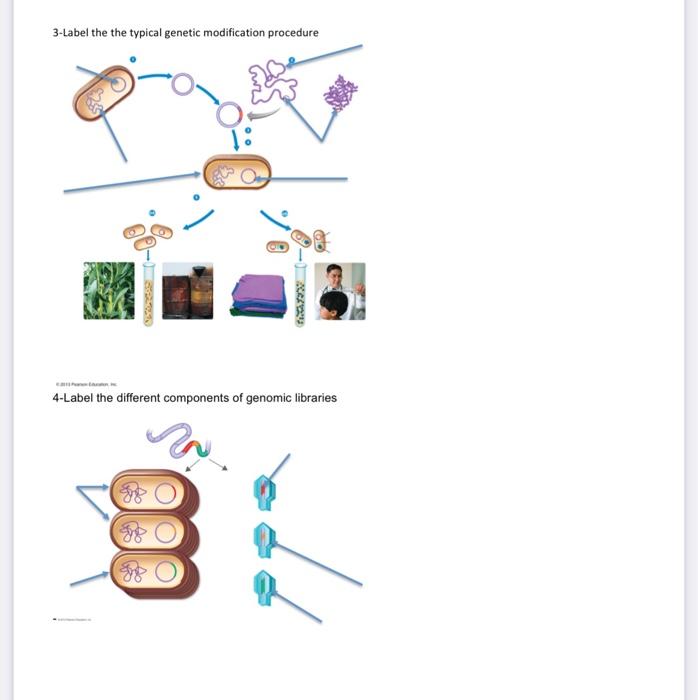
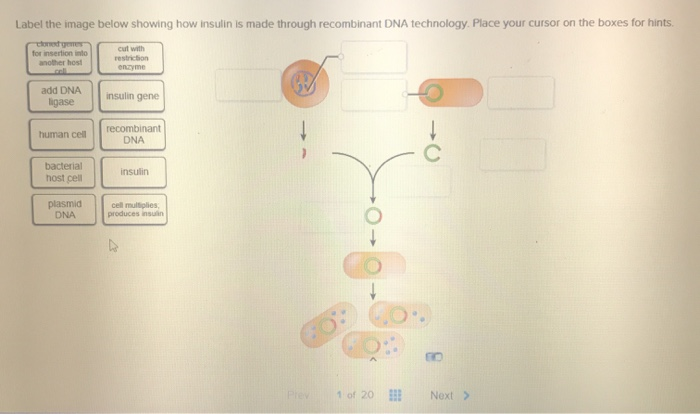
41 label the processes involved in recombinant dna technology.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › HelicaseHelicase - Wikipedia Many cellular processes, such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, recombination, DNA repair, and ribosome biogenesis involve the separation of nucleic acid strands that necessitates the use of helicases. Some specialized helicases are also involved in sensing of viral nucleic acids during infection and fulfill a immunological function. Recombinant DNA technology Flashcards | Quizlet what recombinant DNA technology can be used for -Sequencing the human genome -Cloning the open reading frames of genes for study -Cloning other fragments of DNA for study (promoters etc.) -Expressing proteins in cells to make therapeutic products like human insulin gene cloning isolating, and making many copies of a specific segment of DNA
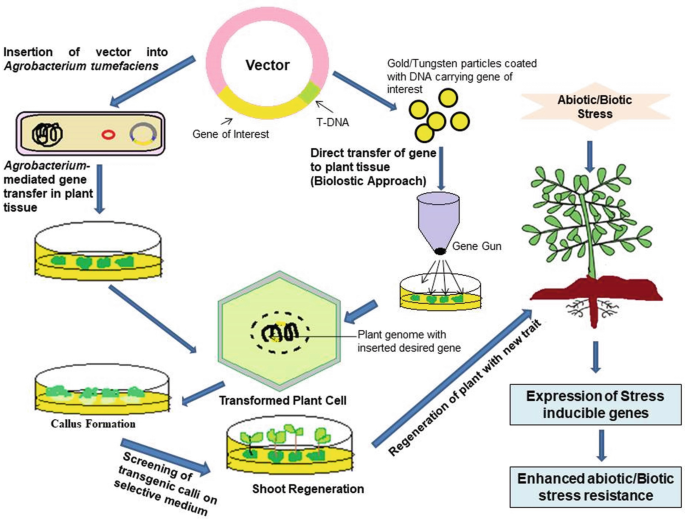
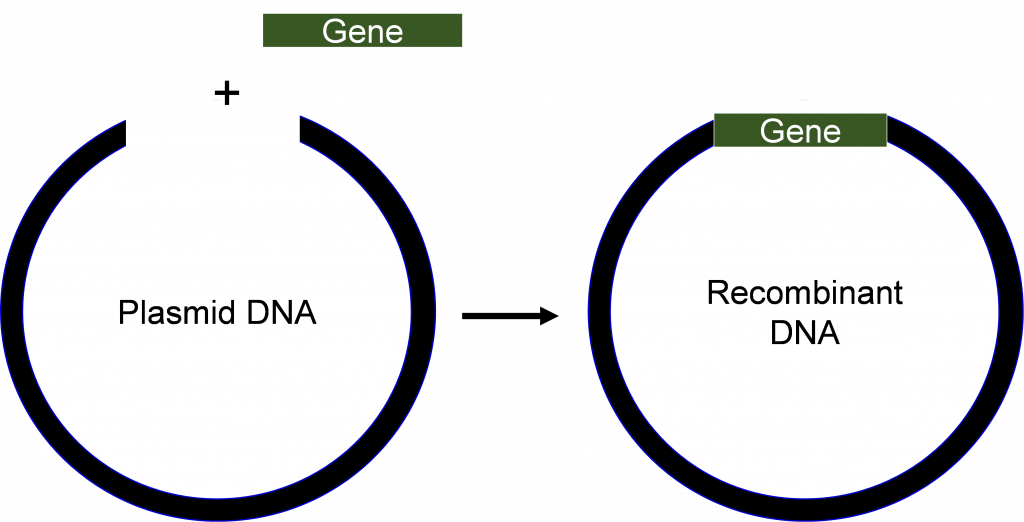
Role of Recombinant DNA Technology to Improve Life - PMC Recombinant DNA technology comprises altering genetic material outside an organism to obtain enhanced and desired characteristics in living organisms or as their products. This technology involves the insertion of DNA fragments from a variety of sources, having a desirable gene sequence via appropriate vector [ 12 ].
Label the processes involved in recombinant dna technology.
What Is Recombinant DNA Technology? - ThoughtCo Recombinant DNA technology combines DNA from different sources to create a different sequence of DNA. Recombinant DNA technology is used in a wide range of applications from vaccine production to the production of genetically engineered crops. As recombinant DNA technology advances, technique precision must be balanced by ethical concerns. 5 Steps in Recombinant DNA Technology or rDNA Technology Step V: Multiplication or expression of the gene of interest. The objective of gene cloning is either to make numerous copies of the desired gene or to produce the protein coded by the desires gene. The inserted gene along with the vector will replicate inside the host so that many copies of the desired gene is synthesized. Recombinant DNA Technology (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion Suitable host cells are selected and the rec DNA molecule so formed [in step (iii)] is introduced into these host cells. This process of entry of rec DNA into the host cell is called transformation. Usually selected hosts are bacterial cells like E. coli, however yeast, fungi may also be utilized. (v) Selection of transformed host cells:
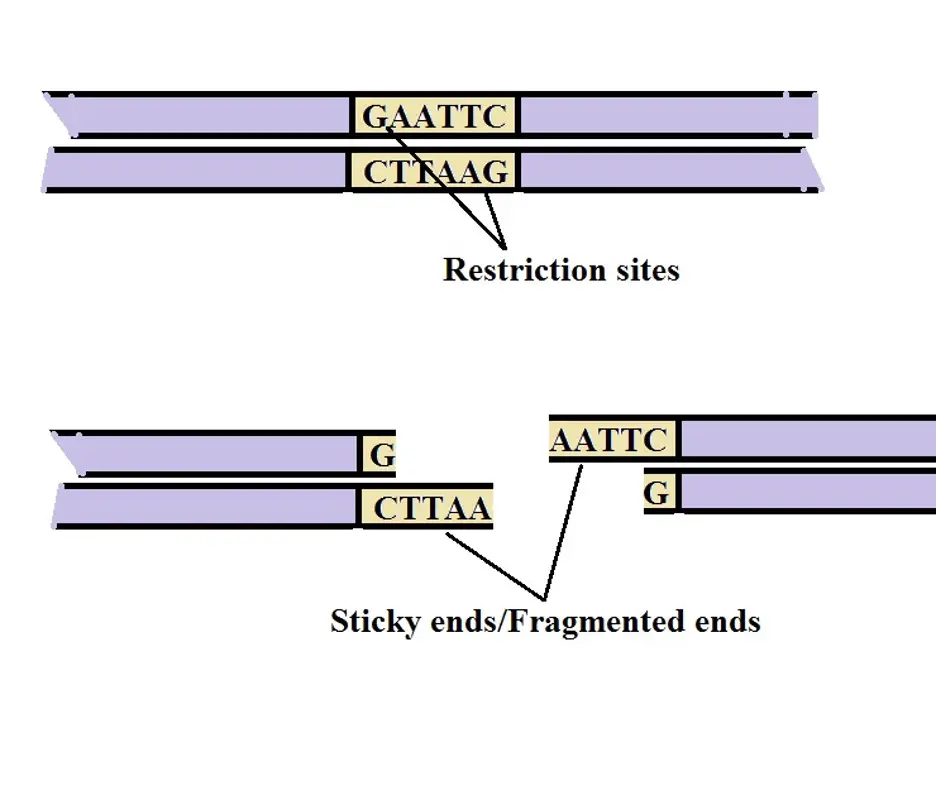
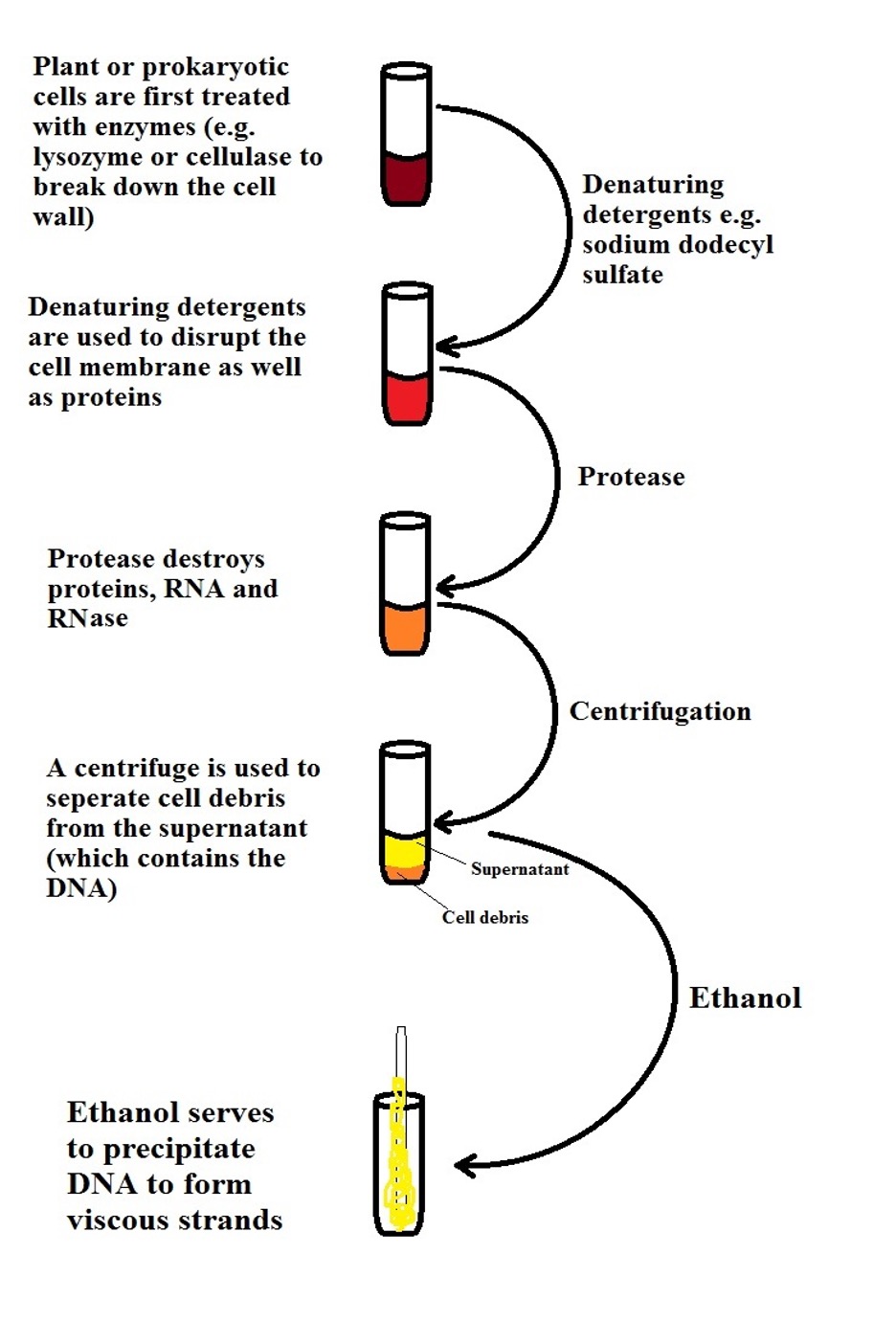
Label the processes involved in recombinant dna technology.. 7 Steps Involved in the Preparation of a Recombinant DNA The following points highlight the seven steps involved in the preparation of a recombinant DNA. The steps are: 1. Selection of Target DNA 2. Selection of a Suitable Cloning Vector DNA or Vehicle DNA 3. Selection of Restriction Endonucleases 4. Procedure for Production of Recombinant DNA (rDNA) 5. Introduction of the rDNA into a Host Cell 6. us.vwr.com › store › productPowerSoil® DNA Isolation Kits, MO BIO Laboratories | VWR This enables samples to be used for the most demanding downstream applications, including PCR, QPCR, and next generation sequencing. When choosing between the PowerSoil® DNA Isolation Kit and the UltraClean® Soil DNA Isolation Kit, use this kit for samples that are very high in humic content. Recombinant DNA - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Recombinant DNA is the method of joining two or more DNA molecules to create a hybrid. The technology is made possible by two types of enzymes, restriction endonucleases and ligase. A restriction endonuclease recognizes a specific sequence of DNA and cuts within, or close to, that sequence. By chance, a restriction enzyme's recognition sequence ... Recombinant DNA Technology - Goals, Process, Tools and ... - VEDANTU Keeping that in mind, let's proceed to find the steps involved in rDNA technology. Process of RDNA Technology These are its process - DNA isolation DNA is isolated in its pure form, which means they are devoid of other macromolecules. Cutting of DNA For this step, the restriction enzymes are quite vital.
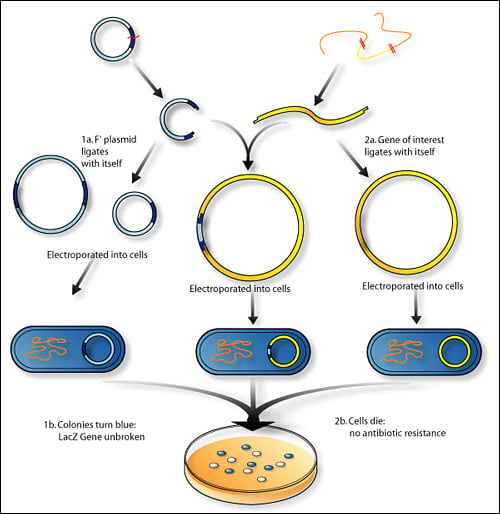
Recombinant DNA Technology and its Applications: A Review Abstract. Biotechnology which is synonymous with genetic engineering or recombinant DNA (rDNA) is an industrial process that uses the scientific research on DNA for practical applications. rDNA is ... Solved Bacterial cell ?? DNA containing gene of interest - Chegg DNA containing gene of interest Isolate fragment with the gene of interest Insert plasmid and gene into bacterium Bacterial chromosome Isolate plasmid Plasmid Insert gene into plasmid Gene of interest Culture bacteria. Enzymatically cleave DNA into fragments Harvest copies of gene to insert into plants or animals Harvest proteins coded by gene Recombinant DNA Technology (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The technique of recombinant DNA can be used as follows: 1. It can be used to elucidate molecular events in the biological process of cellular differentiation and ageing. 2. This can also be utilised in making gene maps with precision. 3. This can be used to spell out the complete nucleotide sequence of genome of various organisms including humans. Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology - Toppr-guides This process involves multiple steps that have to proceed in a specific sequence to generate the desired product. Let's understand each step in detail. Table of content 1 Suggested Videos 2 1. Isolation of Genetic Material 3 2. Restriction Enzyme Digestion 4 3. Amplification Using PCR 5 4. Ligation of DNA Molecules 6 5.
Biology - Recombinant DNA Technology Flashcards | Quizlet - Combining of the DNA from two organisms - recombinant DNA - Resulting organism - genetically modified organism - Powerful technique as can mix DNA from different species Summarise the steps involved in recombinant DNA technology? Principle of Recombinant DNA Technology (4 Steps) - Biology Discussion The principle of recombinant DNA technology involved four steps. The four steps are: (1) Gene Cloning and Development of Recombinant DNA (2) Transfer of Vector into the Host (3) Selection of Transformed Cells and (4) Transcription and Translation of Inserted Gene. Recombinant DNA - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf - National Center for ... The first step in the development of recombinant DNA technology was the characterization of restriction endonucleases — enzymes that cleave DNA at specific sequences. These enzymes were identified in bacteria, where they apparently provide a defense against the entry of foreign DNA (e.g., from a virus) into the cell. The different steps of recombinant DNA technology are given below ... Down streaming process i.e; Selection of the transformed host cells and identification of the clone containing the desired gene/DNA fragment. ... Similar questions. One of the following is not a step involved in recombinant DNA technology. Medium. View solution > (a) Mention the role of vectors in recombinant DNA technology. Give any two ...
embryo.asu.edu › pages › green-fluorescent-proteinGreen Fluorescent Protein | The Embryo Project Encyclopedia Jun 11, 2014 · Using DNA recombinant technology, scientists combine the Gfp gene to a another gene that produces a protein that they want to study, and then they insert the complex into a cell. If the cell produces the green fluorescence, scientists infer that the cell expresses the target gene as well.
Recombinant DNA Technology - Process & Applications of rDNA ... - BYJUS Recombinant DNA technology is a technique that alters the phenotype of an entity (host) when a genetically modified vector is introduced and incorporated into the genome of the host. Thus, the process entails introducing a foreign fragment of DNA into the genome containing the desired gene.
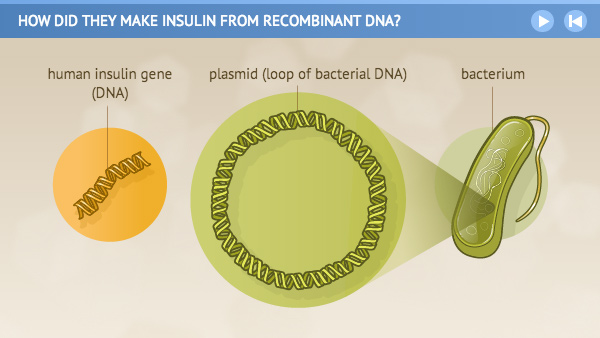
How did they make insulin from recombinant DNA? Recombinant DNA is a technology scientists developed that made it possible to insert a human gene into the genetic material of a common bacterium. This "recombinant" micro-organism could now produce the protein encoded by the human gene. Scientists build the human insulin gene in the laboratory. Then they remove a loop of bacterial DNA ...
recombinant DNA | Definition, Steps, Examples, & Invention recombinant DNA, molecules of DNA from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science, medicine, agriculture, and industry. Since the focus of all genetics is the gene, the fundamental goal of laboratory geneticists is to isolate, characterize, and manipulate genes.
Recombinant DNA Technology- Definition, Steps, Applications - Microbe Notes Polymerase Chain Reaction or PCR is a method of making multiple copies of a DNA sequence using the enzyme - DNA polymerase in vitro. It helps to amplify a single copy or a few copies of DNA into thousands to millions of copies. PCR reactions are run on 'thermal cyclers' using the following components: Template - DNA to be amplified
› drugsatfda_docs › labelENBREL (etanercept) - Food and Drug Administration Etanercept is produced by recombinant DNA technology in a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) mammalian cell expression system. It consists of 934 amino acids and has an apparent molecular weight of approximately 150 kilodaltons. ENBREL® single-use prefilled syringes are available in 25 mg (0.51 mL of a 50 mg/mL solution
Micro Exam 3 Flashcards | Quizlet an anabolic polymerization process Nucleotides used in the replication of DNA __________. carry energy, are present in cells as triphosphate nucleotides, and are found in four forms, each with a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a base A nucleotide is composed of __________. five-carbon sugar, phosphate, and a nitrogenous base
› products › primary-antibodiesAcetylated-Lysine Antibody | Cell Signaling Technology DNA should be digested to a length of approximately 150-900 bp (1 to 5 nucleosomes). To determine DNA concentration, transfer 2 µl of purified DNA to 98 µl nuclease-free water to give a 50-fold dilution and read the OD 260. The concentration of DNA in µg/ml is OD 260 x 2,500. DNA concentration should ideally be between 50 and 200 µg/ml.
Recombinant DNA technology Flashcards - Questions and Answers | Quizlet Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutation of the CFTR gene. CFTR protein is defective so normal CFTR allele can be inserted into the DNA of the sufferer. A chromosome in cells of respiratory system. The DNA is inserted into a vector called a liopsome and it is taken as spray. Harmless viruses can also be used however not all cells take up virus.
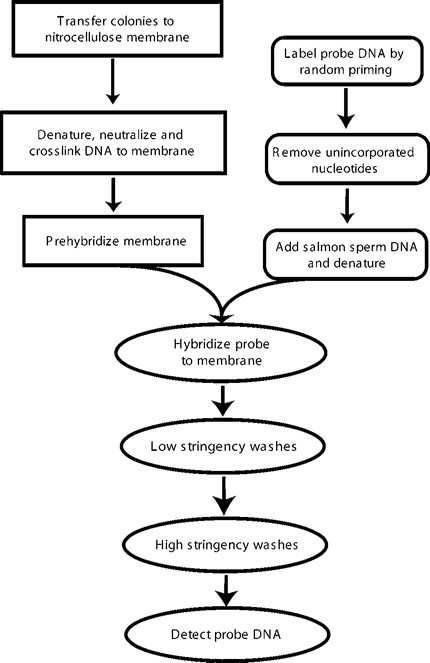
Chapter 8 Recombinant DNA Technology Flashcards | Quizlet What is recombinant DNA technology? Describe the process. Technique that allows DNA to be combined from different sources; also called gene or DNA splicing. Recombinant DNA is an important technique for many gene-cloning applications. 1) Isolate plasmid: probe is used to isolate the gene of interest
wolfson.huji.ac.il › purification › Purification_ProtocolsPURIFICATION PROTOCOLS - wolfson.huji.ac.il Dec 14, 2017 · BIA Separations CIM ® Monolithic Columns based on CIM Convective Interaction Media ® Technology; suitable for purification of large biomolecules such as viruses (viral vectors and vaccines), DNA (plasmid DNA) and larger proteins (Immunoglobulins G and M, pegylated proteins). CIM ® Monolithic Columns exhibit unrivaled characteristics in terms ...
An Introduction to Recombinant DNA - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Recombinant DNA is the general name for taking a piece of one DNA, and. and combining it with another strand of DNA. Thus, the name recombinant! Recombinant DNA is also sometimes referred to as "chimera." By combining two or. more different strands of DNA, scientists are able to create a new strand of DNA.
Recombinant DNA (Rdna) Technology Involves The Following Stages Recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology involves the following six stages: 1. Isolation of the Genetic Material (DNA) 2. Cutting of DNA at Specific Locations 3. Amplification of Gene of Interest Using PCR 4. Preparation and Insertion of Recombinant DNA into the Host Cell/Organism 5. Obtaining the Foreign Gene Product! 1.
Solved Parta Label the processes involved in recombinant DNA - Chegg Expert Answer. 100% (6 ratings) SOLUTION: Proces …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Parta Label the processes involved in recombinant DNA technology Drag the appropriate Labels to their respective targets. Reset Help DNA containing eo M Culture bacteria.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Tissue_plasminogen_activatorTissue plasminogen activator - Wikipedia Tissue plasminogen activator (abbreviated tPA or PLAT) is a protein involved in the breakdown of blood clots. It is a serine protease (EC 3.4.21.68) found on endothelial cells, the cells that line the blood vessels. As an enzyme, it catalyzes the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, the major enzyme responsible for clot breakdown. Human tPA ...
With the help of a neat and labelled diagram describe steps in ... The basic steps involved in the process of DNA technology are as follows. (i) The genomic DNA is isolated from a donor. (ii) Using restriction enzymes such as endonucleases the DNA is fragmented. Endonuclease enzymes are known as molecular scissors as they produce nick in the DNA fragment at the desired place. (iii) The fragments were taken out ...
Recombinant DNA Technology- Tools, Process, and Applications - BYJUS The complete process of recombinant DNA technology includes multiple steps, maintained in a specific sequence to generate the desired product. Step-1. Isolation of Genetic Material. The first and the initial step in Recombinant DNA technology is to isolate the desired DNA in its pure form i.e. free from other macromolecules. Step-2.
Recombinant DNA Technology (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion Suitable host cells are selected and the rec DNA molecule so formed [in step (iii)] is introduced into these host cells. This process of entry of rec DNA into the host cell is called transformation. Usually selected hosts are bacterial cells like E. coli, however yeast, fungi may also be utilized. (v) Selection of transformed host cells:
5 Steps in Recombinant DNA Technology or rDNA Technology Step V: Multiplication or expression of the gene of interest. The objective of gene cloning is either to make numerous copies of the desired gene or to produce the protein coded by the desires gene. The inserted gene along with the vector will replicate inside the host so that many copies of the desired gene is synthesized.
What Is Recombinant DNA Technology? - ThoughtCo Recombinant DNA technology combines DNA from different sources to create a different sequence of DNA. Recombinant DNA technology is used in a wide range of applications from vaccine production to the production of genetically engineered crops. As recombinant DNA technology advances, technique precision must be balanced by ethical concerns.

























Post a Comment for "41 label the processes involved in recombinant dna technology."