41 the descending limb of the nephron loop quizlet
What Are the Functions of Nephron? | Med-Health.net The nephron is the basic functional and structural unit found in the kidneys. Its main functions include regulating the concentration of sodium salts and water by filtering the kidney's blood, excreting any excess in the urine and reabsorbing the necessary amounts. It also regulates blood pressure and volume, controls the levels of ... What does the ascending loop of Henle transport? The ascending limb has a thin and a thick segment. The ascending limb drains urine into the distal convoluted tubule. What is the function of the ascending loop of Henle quizlet? The thick ascending limb of nephron loop connects with the distal convoluted tubule, which connects with the urine connecting duct. The loop of henle dips down into ...
Where are nephrons located quizlet? Explained by FAQ Blog What is a nephron and what does it do quizlet? Nephron. Functional unit of the kidney, where urine is produced. ... The ascending limb of loop of Henle is divided into 2 segments: Lower end of ascending limb is very thin and is lined by simple squamous epithelium.

The descending limb of the nephron loop quizlet
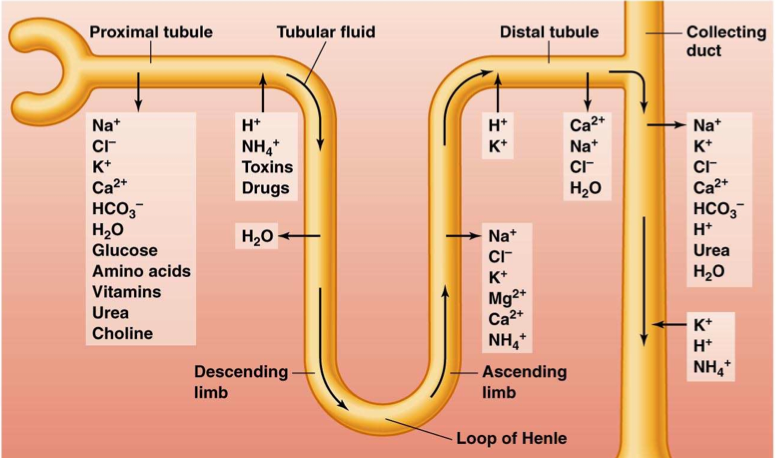
The Loop of Henle - Function - Diuretics - TeachMePhysiology The descending limb is highly permeable to water, with reabsorption occurring passively via aquaporin-1 (AQP1) channels. Very low amounts of urea, sodium (Na+) and other ions are also reabsorbed. As mentioned above, water reabsorption is driven by the counter-current multiplier system set up by the active reabsorption of sodium in the TAL. Urinary System Quiz Questions And Answers - ProProfs Quiz You can share the quiz with your friends or other medical professionals if you like it. Questions and Answers 1. The ___________ arteries supply the kidneys with blood. 2. The bladder is lined with ______________ epithelium. A. Simple columnar B. Transitional C. Stratified squamous D. Simple cuboidal E. Pseudostratified columnar 3. Where does reabsorption of water occur in the nephron? The loop of Henle is shaped like a "U", with a descending limb and an ascending limb. Filtered fluid first passes through the descending limb. Filtered fluid first passes through the descending limb. Here, water flows out of the tubule into the surrounding tissue, as the walls of the nephron are permeable to water in this part of the structure.
The descending limb of the nephron loop quizlet. exam 3 Flashcards | Quizlet Which of the following is true of the countercurrent multiplier action of the nephron loop? As fluid travels down the descending limb of the nephron loop, water leaves the tubule and enters the medullary tissue (ECF). T/F: the ability of the collecting duct to reabsorb water depends on the increased salinity of the renal medulla True SYS PHYS FINAL Flashcards | Quizlet At which point in the nephron is there the highest concentration of sodium Top of Ascending limb of the loop of henle Bowmans capsule Bottom of Descending limb of the loop of henle Collecting Duct. ... Quizlet Live. Quizlet Checkpoint. Quizlet Learn. Explanations. Flashcards. Mobile. Quizlet Plus. EXS Exam #4 (renal II) Flashcards | Quizlet three renal processes 1) glomerular filtration 2) tubular reabsorption 3) tubular secretion glomerular filtration initial filtration of incoming blood, indiscriminate process tubular reabsorption removal of filtered substances from lumen, highly discriminate tubular secretion addition of substances to lumen (reabsorbed), highly discriminate What happens in the thick ascending limb? - TimesMojo Thick ascending limbs of Henle's loop have at least three major roles: (1) They reabsorb sodium chloride which dilutes the urine. … (3) They reabsorb large amounts of potassium, calcium, and magnesium in an energy-efficient manner. Is the ascending limb impermeable to water? The ascending limb (where loop diuretics work) is impermeable to water.
EOF 4-27-22 renal phys II Flashcards | Quizlet 1. within LDT, CT, medullary collecting ducts, & epithelial cells --> ADH attaches to V2 receptor (transcellular) 2. V2 receptor uses energy to make protein kinase in cell 3. protein kinase phosphorylates aquaporin 4. aquaporin-2 is inserted in apical membrane to increase water reabsorption what hormone is the opposite of ADH/AVP & RAAS? Learning plan 4 and 5 homework assignment - Flashcards 1. ascending limb - impermeable to water - permeable to solutes - tubular fluid osmolarity decreases as it passes through 2. descending limb - impermeable to solutes - permeable to water - tubular fluid osmolarity increases as it passes through Join StudyHippo to unlock the other answers Join Studyhippo Join with googlejoin with facebook question In the ascending limb of the loop of henle the? The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is a direct continuation from the descending limb of loop of Henle, and one of the structures in the nephron of the kidney. The ascending limb has a thin and a thick segment. The ascending limb drains urine into the distal convoluted tubule.
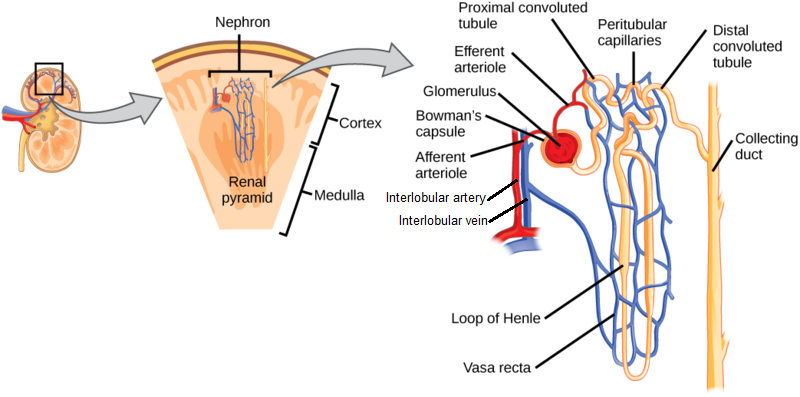
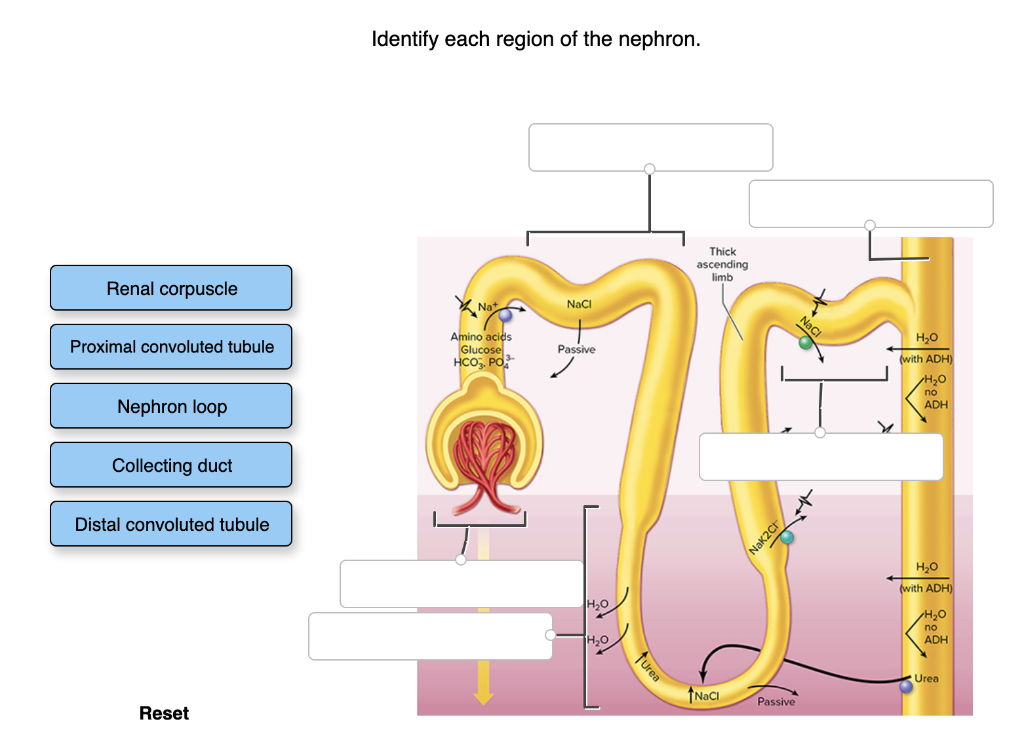
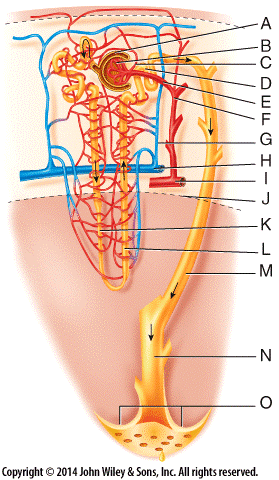
descending vs ascending loop of henle - Hunting In Montana The key difference between ascending and descending loop of Henle is that ascending loop of Henle is the thicker segment of the loop of Henle located just after the sharp bend of the loop while descending loop of Henle is the thinner segment located just before the sharp bend of the loop.. Where are nephrons located? - TimesMojo (A) The nephron consists in the glomerulus (G) and the renal tubule, which includes the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), the proximal straight tubule (PST), the thin descending limb (tDL), the thin ascending limb (tAL), the thick ascending limb (TAL), the distal convoluted tubule (DCT), the connecting tubule (CNT), … During tubular secretion fluid moves where quizlet? Where is most water reabsorbed in the nephron? The majority of water reabsorption that occurs in the nephron is facilitated by the AQPs. Most of the fluid that is filtered at the glomerulus is then reabsorbed in the proximal tubule and the descending limb of the loop of Henle. Urinary system chapter 17 Flashcards | Quizlet The Distal, farthest from renal corpuscle. Even though it is short, it plays a key role in regulating extracellular fluid volume and electrolyte homeostasis. nephron loop (loop of Henle) U-shaped structure consisting of two limbs, an descending limb, Water can leave, solutes can not, an ascending limb, Water can not leave, solutes can leave
Kidney histology: Nephron, loop of Henle, functions | Kenhub The nephron loop is the U-shaped bend of a nephron which extends through the medulla of the kidney. Histologically, it consists of two parts; thin descending and thin ascending limbs. Both limbs are composed of simple squamous epithelium. The cells have few organelles, little to no microvilli and low secretion abilities.
What is reabsorbed in the ascending loop of henle? What substance is reabsorbed in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle quizlet? Na+ is actively being pumped out of thick ascending limb of LOH to be reabsorbed. This gradient is used by the collecting ducts under the influcence of ADH to control the amount of water that is excreted or reabsorbed.
Where does reabsorption of water occur in the nephron? The loop of Henle is shaped like a "U", with a descending limb and an ascending limb. Filtered fluid first passes through the descending limb. Filtered fluid first passes through the descending limb. Here, water flows out of the tubule into the surrounding tissue, as the walls of the nephron are permeable to water in this part of the structure.
Urinary System Quiz Questions And Answers - ProProfs Quiz You can share the quiz with your friends or other medical professionals if you like it. Questions and Answers 1. The ___________ arteries supply the kidneys with blood. 2. The bladder is lined with ______________ epithelium. A. Simple columnar B. Transitional C. Stratified squamous D. Simple cuboidal E. Pseudostratified columnar 3.
The Loop of Henle - Function - Diuretics - TeachMePhysiology The descending limb is highly permeable to water, with reabsorption occurring passively via aquaporin-1 (AQP1) channels. Very low amounts of urea, sodium (Na+) and other ions are also reabsorbed. As mentioned above, water reabsorption is driven by the counter-current multiplier system set up by the active reabsorption of sodium in the TAL.



























Post a Comment for "41 the descending limb of the nephron loop quizlet"