42 nucleus electron micrograph labelled
Solved Please label the electron micrograph to assess your | Chegg.com Question: Please label the electron micrograph to assess your knowledge of the structure and function of a cell's nucleus nuclear pore endoplasma reticulum chromatin nucleolus nuclear envelope This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (3 ratings) 1 ) Nuclear envelo … View the full answer › pmc › articlesCell mechanics and the cytoskeleton - PMC Jan 28, 2010 · b, The micrograph (left) shows fluorescently labelled actin filaments (white) that have polymerized inside the vesicle and have assembled into a fascin-crosslinked network. Scale bar, 5 μm. The diagram (right) is a schematic depiction of the actin-filament network present in the inset box of the micrograph.
Tomography of the cell nucleus using confocal microscopy and medium ... The migration of BrUTP-labeled rRNAs was observed in α-amanitin (an inhibitor of RNA polymerase II)-treated cells which were pulse-labeled for 15 min and then chased for 2, 15, 30 and 90 min ().Visualization of the same cell firstly by phase-contrast microscopy and secondly by confocal microscopy showed that rRNA synthesis takes place in tiny structures within nucleoli.
Nucleus electron micrograph labelled
Transmission Electron Micrograph [Transmission Electron Micrograph] - 18 images - transmission electron microscopy, brief introduction of transmission electron microscopy authorstream, scanning transmission electron microscopy springerlink, cin2003 ian roberts mast cells in the kidney, PDF Electron Micrographs (EMs) for laboratories in A215, Basic Human Anatomy There are distinct differences between cilia and microvilli to be seen in electron micrographs: - Cilia are larger (the cilium labeled C about 2.5 microns along its length is probably 5 to 10 microns long); - Cilia contain microtubules, by which they can move. [Immune electron microscope determination of the localization of ... The number of particles observed over diffuse chromatin equals to 50-80% against the label in fibroblast cytoplasm. In contrast, the label used to be absent over the E. coli nucleoid. The presence of TRS in the fibroblast nucleus may evidence in favour of a possible regulatory role of TRS in eukaryots. MeSH terms
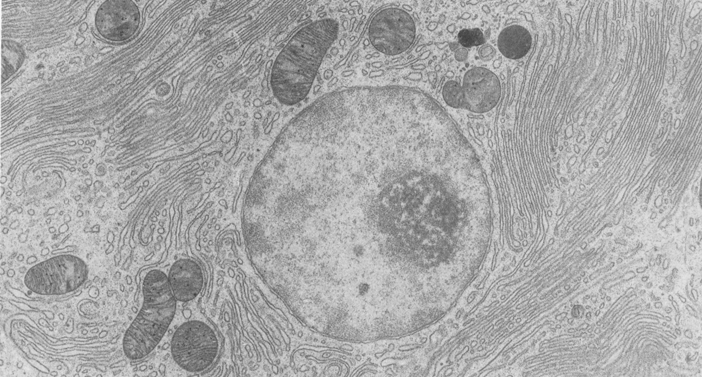
Nucleus electron micrograph labelled. animal cell under electron microscope labelled Animal Cell Diagram Under Microscope Labeled. Here is an electron micrograph of an animal cell with the labels superimposed. An animal cell represents an eukaryotic cell in which true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria Golgi bodies and lysosomes are present. Function cell does in the body. Labeling the Cell Flashcards | Quizlet Label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus. membrane bound organelles golgi apparatus, mitochondrion, lysosome, peroxisome, rough endoplasmic reticulum nonmembrane bound organelles ribosomes, centrosome, proteasomes cytoskeleton includes microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules Identify the highlighted structures Ultrastructure of Rat Rostral Nucleus of the Solitary Tract Terminals ... Electron micrographs of immunogold staining for glutamate in adjacent thin sections through anterogradely labeled Glut+ terminals (#1-#4) in the parabrachial nucleus (PBN, A-D) and medullary reticular formation (RF, E-H) after tracer injection in the rNST. Postsynaptic targets of Glut+ labeled terminals (boutons) are different in the PBN ... › natural-sciences › gr9Natural Sciences Grade 9 - Grade 7-9 Workbooks Learners are often only exposed to schematic diagrams of cells which present an idealised view of the cell. They then find it very difficult to identify these structures within a micrograph of an actual cell. Encourage your learners to take note of how the diagram below was drawn and how it differs to the micrograph of the nucleus.
Label This Transmission Electron Micrograph : TEM of chloroplast from ... Provide the labels for the electron micrograph in figure 12.8. Label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus. Label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus. Transmission electron microscopy (tem) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. Nucleus: Definition, Origin, Structure, Functions The nucleolus is a prominent, spherical, colloidal, acidophilic structure found in the nucleus of a typical cell. It is mainly composed of phosphoproteins and RNA. The electron micrograph and immunocytological techniques show that three distinct regions are observed in the nucleolus. Electron Micrograph of a Lymphocyte Pricing. Price for. Choose Usage Printed publication (book, brochure, journal, etc.) Trial Exhibits and Materials Slide Presentation (Non-web or authenticated login if Web) Electronic Formats Posters Tee Shirts, Novelties Student Lo-res Presentation/Poster, Thesis, Dissertation. Product Description: Solved Label the transmission electron micrograph of the - Chegg Transcribed image text: Label the transmission electron micrograph of the cell. 0 Nucleus rences Mitochondrion Heterochromatin Peroxisome Vesicle ULAR bumit Click and drag each label into the correct category to indicate whether it pertains to the cytoplasm or the plasma membrane.
Plant Cell Nucleus Electron Micrograph : Cell And Organelles Dr Jastrow ... The nucleus (plural = nuclei) figure 7.14 at left a transmission electron micrograph and at right a labeled diagram of a. An electron micrograph of a cell nucleus showing a densely staining nucleolus. Plant cell, electron micrograph 13 plant cells and tissues 29, 30 fiber 11. Electron Micrograph of a Neutrophil - Netter Images Pricing. Price for. Choose Usage Printed publication (book, brochure, journal, etc.) Trial Exhibits and Materials Slide Presentation (Non-web or authenticated login if Web) Electronic Formats Posters Tee Shirts, Novelties Student Lo-res Presentation/Poster, Thesis, Dissertation. Product Description: Cell Nucleus - function, structure, and under a microscope The nucleus is a key feature that distinguishes eukaryotic cells, including all animals and plants, from prokaryotic cells (bacteria and archaea). The nucleus (plural: nuclei) stores most of the cell's genetic information in the form of DNA, although mitochondria also contain their own DNA in a very small percentage relative to the nucleus. New Tools for Imaging Neutrophils: Work Function Mapping and Element ... Photoemission electron microscopy and imaging X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy are today frequently used to obtain chemical and electronic states, chemical shifts, work function profiles within the fields of surface- and material sciences. Lately, because of recent technological advances, these tools have also been valuable within life sciences.
Nucleus - Electron Micrograph Slide 5 of 36
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Marine_lifeMarine life - Wikipedia Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of the sea or ocean, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries.At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet.
Electron Micrographs of Cell Organelles | Zoology This is an electron micrograph of nucleus. (Fig. 17 & 18): (1) Nucleus was discovered by Brown (1831). (2) It is a characteristic entity of almost all eukaryotic cells except mammalian RBCs. (3) The nucleus is generally one but may also be two, four or many.
Nucleus 19 | Digital Histology Three regions of the nucleolus are visible in this electron micrograph. The pale areas are the nucleolar organizing centers. The most dense areas are the pars fibrosa, which contain newly synthesized primary transcripts of RNA genes. The pars granulosa has a granular appearance and contains maturing ribosomal particles. 33,000x. Main Slide ...
Looking at the Structure of Cells in the Microscope When labeled with fluorescent dyes, they are invaluable for locating specific molecules in cells by fluorescence microscopy (Figure 9-15); labeled with electron-dense particles such as colloidal gold spheres, they are used for similar purposes in the electron microscope (discussed below).
› difference › BacteriaBacteria vs Virus - Difference and Comparison | Diffen Bacteria are single-celled, prokaryotic microorganisms that exist in abundance in both living hosts and in all areas of the planet (e.g., soil, water). By their nature, they can be either "good" (beneficial) or "bad" (harmful) for the health of plants, humans, and other animals that come into contact with them.
idoc.pub › documents › mcgraw-hill-ryerson-biologyMcgraw-hill Ryerson Biology 12 (2011).pdf [jlk97weo2845] For example, the sodium atom, Na, has only one electron in its outer valence shell. Once this electron is given up, the electron shell closer to the sodium nucleus, which already contains eight electrons, becomes the valence shell. When an atom or group of atoms gains or loses electrons, it acquires an electric charge and becomes an ion.
› 44090147 › CambridgeCambridge International AS and A Level Biology Coursebook ... Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
PDF Identifying Organelles from an Electron Micrograph Courtesy of Dr. Julian Thorpe - EM & FACS Lab, Biological Sciences University Of Sussex The electron micrograph displayed below illustrates many of the plant cell characteristics discussed The cell wall, large central vacuole and chloroplasts are clearly visible Also visible is the clearly defined nucleus containing chromatin



Post a Comment for "42 nucleus electron micrograph labelled"